HACKING NEWS
Trump up the US Cyber Arsenal

Trump up the US Cyber Arsenal. The US military had received a “historic” and “never before” funding of USD716 billion budget in mid-August, sealed with US President, Donald Trump’s signature.
The massive military spending might not be the largest in US military history as Trump suggested as US Congress had approved larger funds during the peak of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan during the 2007-2012 period.
Then, why is there a need for these vast military expenditures currently, since the withdrawal of US troops in Iraq? The answer might lie in using this massive military budget to compete against rising military cooperation of Russia and China, as well as deterring their famed cyber-attacks.
Not all the money goes to guns and bombs
It was known that a faction of the military budget capped around at USD 100 million will go to test infrastructure and personnel, including for cybersecurity.
Despite smaller funding as compared to the purchase of 77 F-35 fighter aircrafts, the US military may expand spending on this area after the alleged Russian hacking on 2016 presidential elections as well as the reportedly intellectual thefts conducted by the Chinese hackers on US industry.
As US trade tension with China escalates, there might be more measures introduce to shore up cybersecurity for sensitives industry like arms and defense contractors.
Removal of red tapes on Cyberwar declaration
Along with the signing for the big military, US President Trump had also removed some red tapes in cyberwar declaration.
In the past, the cyberwar was bound by the Obama-administration framework named Presidential Policy Directive 20 (PPD 20), which dictated how and when US can launch cyber-attacks against its enemy in following a multi-agency process of checks and balances.
Apparently, the PPD 20 was replaced by a Trump administration with a more streamline approach, while the details of the new directory remained classified. This could imply now the President of the United States may play a bigger role in the launch of cyber-attacks as compared to previous administration.
United States, the mother of all Weapons of Mass ‘Cyber’ Destruction
US had pioneered a cyber-security agency in 2009 under the name of United States Cyber Command (USCYBERCOM). The entity acts as a unified body plans, coordinates, integrates, synchronizes and conducts activities for military cyberspace operations.
It was heard that since its inception in 2009, the agency has stockpiled numerous ‘cyber weapons’ in its arsenal. Rumour had it that Wannacry, the deadly ransomware attack in May 2017, and NotPetya cyberattack on June 2017 were just exploits developed by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA), which had been stolen and used by malicious hackers to infect computer systems.
Verdict
In the world of Internet, the US always seem to have the cutting edge. After all, the US military played a big role in its development of the Internet in linking various military outposts in an unfortunate event of a nuclear fallout.
Thus, they may hold all the ‘backdoors’ and know which loop holes to exploit for cyber-warfare. As in all war, both ammunition and arsenals need money, and the best prepared army tend to fare better in warfare just as the saying goes, “Fortune favours the prepared mind.”
HACKING NEWS
The APT attacks hitting East Asia

The APT attacks hitting East Asia
East Asia have been targeted by a stream of cyber-attacks carried about by an advanced persistant threat (APT) group. The group goes by several names such as Tick, Brzone Butler and Redbaldknight.
The APT group’s main targets are South Korea and Japan. This current wave of Datper malware attacks is written in Delphi and is capable of executing shell commands to gain information from the infected machine, such as hostnames and drive information.
Security researchers from Cisco Talos have stated It is not yet known how the attacks are being conducted since command and control (C2) servers in question are not active. However, they say it’s possible the malware is being delivered using web-based attacks such as drive-by downloads, or by watering hole attack. Watering hole attacks is a security exploit in which the attacker seeks to compromise a specific group of end users by infecting websites that members of the group are known to visit.
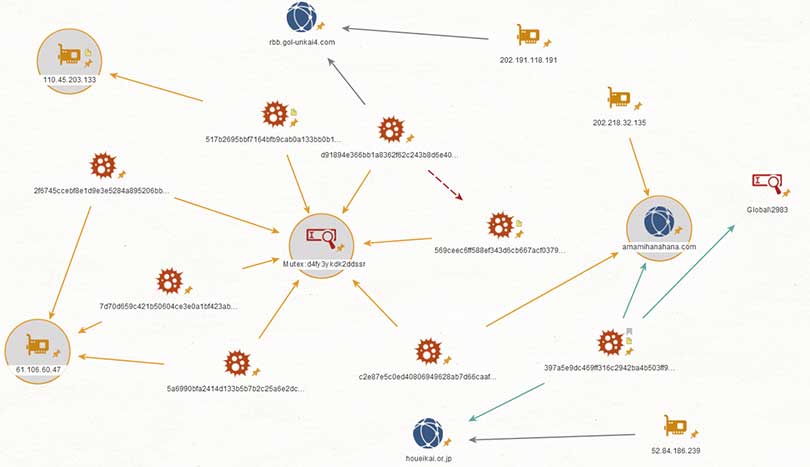
Could this signal the re-emergence of Comment Crew
A fresh wave of APT cyber-attacks has hit South Korea, but also US and Canada, causing some to believe this could spell the re-emergence of Chinese government backed hacking group Comment Crew. Security company McAfee claimed they have discovered a new hacking campaign that focuses on cyberespionage and data reconnaissance.
Comment Crew or otherwise known as Shanghai Group or APT1 is thought to be responsible for the majority of China’s cyber-attacks since 2006. In 2013 they were linked to the successful hacks of over 100 US companies, but vanished soon after the exposure, along with hundreds of terabytes of data. The Chinese government maintains that they do not sponsor hacking and claim to be a victim to hacking campaigns themselves.
McAfee has found malware that reuses some of the code that was uses in a campaign called Seasalt that was introduced by APT1 around 2010. The reason this is interesting is because this code was never released publicly, lending authority to McAffee’s claims.
A recent campaign, named Operation Oceansalt has been linked to Comment crew. Operation Onceansalt started in May this year and was seen to be targeting Korean speaker with a data reconnaissance implant. Four more waves have since been detected, aimed against companies in South Korea, the United States and Canada.
The Oceansalt implant gives attackers full control of any system or network it is connected to, however, is mainly used for espionage activity. McAffee acknowledged that the implant allows for information to be sent to a control server and commands can also be executed on infected machines, however the full extent of its purpose is not known.
The waves of attacks
The first wave of attacks happened when a South Korean website was compromised, allowing for a spear-phishing campaign to take place. This was done through Microsoft excel email attachments.
For the first two waves of the attack the targets were South Korean public infrastructure officials. The third round of malware documents was distributed from another compromised South Korean website, and the content related to the financials of the Inter-Korean Cooperation Fund.
In the fourth wave involved the targeting of investment, healthcare, banking and agriculture industries in the US and Canada. There are few details around the extent or damage of this wave.
The fifth wave primarily targeted South Korea and the United States using Oceansalt implant.
Although the full motive of the attack is unclear, there is speculation that it could be financial, or a small part of a much larger attack.
BREAKING NEWS
Ad Clicker Disguised as a Google Photos App has been Hosted on Microsoft Store.

Ad Clicker Disguised as a Google Photos App has been Hosted on Microsoft Store.
A malicious app called “Album by Google Photos” was found to be hosted on the Microsoft store. The app was pretending to be part of Google Photos, but was in fact an ad clicker that generates hidden adverts within the Windows 10 Operating System.
The ad clicker app seemed credible to users because of its name, and also the fact it claimed to be created by Google LLC, Google’s actual Microsoft store account is Google Inc, but it looks unsuspecting to users. Microsoft came under some criticism for not realising the app was actually malicious software since the user reviews did highlight that the app was fake, with plenty of 1* reviews. One review states “ My paid Anti-malware solution detected several attempts to download malware by this app. Watch out”. The App was first released on the Microsoft store in May.
What did the application do?
The “Album by Google Photos” app is a Progressive Web Application (PWA), which acts as the front end for Google Photos and includes a legitimate login screen. Hidden in the app bundle is also an ad clicker which runs in the background and generates income for the app developers.
The app connects to ad URLS, and the ads were very similar to what users would see from typical adware, including tech support scams, random chrome extensions, fake flash and java installs and general low-quality sites.
Microsoft haven’t commented how this app managed to pass the Microsoft review process before ending up on the store. This is somewhat concerning since it could mean other malicious apps of a similar nature have flown under the radar and are still infecting user’s computers. We are waiting for Microsoft to comment on the issue.
HACKING NEWS
How to guide: Check if your Facebook Account has been hacked?

How to guide: Check if your Facebook Account has been hacked?
At the end of September, it was revealed that a Facebook security flaw allowed the access tokens of over 50 Million accounts to be stolen. Access tokens allow users to stay signed in on devices, rather than signing in every time they interact with a Facebook app. On Friday 12 October, after weeks of investigation, Facebook reported that the actual number of accounts affected was 30 million, not 50.
The investigation into how this was made possible, and the extent of the data stolen is still ongoing, but Facebook have said there is no need for users to log out or change their password. Facebook forced 90 million users to log out when the breach was discovered.
Users can use this page to check if they were one of the accounts affected in the incident, as well as read any recent findings from the investigation. When you visit page, if you are not one of the affected users it will tell you this in a statement towards the bottom of the page, and there is no further action required from you other than remaining security conscious when it comes to passwords and such. You will also see a message saying your account hasn’t been compromised if you are one of the one million users to who their tokens stolen but information remained safe.
If you fall into the other 29 million users camp, then you will see one of two messages, depending on the level of your information that was stolen. Fifteen million users had their name, email addresses and phone numbers compromised by hackers. While this is serious enough itself, the other 14 million have a more serious data breach problem.
The other 14 million have had the above information stolen, as well as their username, date of birth, devices you use, gender, language settings and possibly more data such as religious and political views. It’s also possible that they accessed your 10 most recent locations and 15 most recent searches, giving a detailed window into your online presence.
There is currently no evidence that hackers used the vulnerability to attack third-party apps and services to gather more information, which was technically possible. Facebook also continues to report that no passwords of credit card information has been compromised. We are yet to see the full fallout from the breach, but there is also evidence that Facebook logins are being sold on the dark web.
While that data is now out there in the hands of attackers, Facebook has used their support page to offer some advice on avoiding phishing schemes. This is a good move from Facebook, but it doesn’t make up for the grievous level of the data breach and the users it has left vulnerable to tailored phishing attacks now their data is out there.
Photo by Glen Carrie on Unsplash
-
 GAME REVIEW7 years ago
GAME REVIEW7 years agoTop Hacking Simulator Games Every Aspiring Hacker Should Play: Part 1
-

 DEALS7 years ago
DEALS7 years agoGreat Ethical Hacking Courses for Beginners
-

 HACKING NEWS7 years ago
HACKING NEWS7 years agoThe APT attacks hitting East Asia
-

 GAME REVIEW7 years ago
GAME REVIEW7 years agoHacknet Review
-

 BREAKING NEWS7 years ago
BREAKING NEWS7 years agoUK Fines Facebook over Cambridge Analytica Scandal
-

 BREAKING NEWS7 years ago
BREAKING NEWS7 years agoUS Online Retail Company suffered a data breach affecting 6.5 million customers
-

 HOW TO7 years ago
HOW TO7 years agoHow To Become an Ethical Hacker – Beginners Guide
-

 DEALS7 years ago
DEALS7 years agoMusic, Voice and Sound interface kits: What you need to know


